The Tribunal was given authority to prosecute persons responsible for specific crimes committed since January 1991 in the territory of what is referred to as the former Yugoslavia.
What is meant by the term former Yugoslavia is the territory that was up to 25 June 1991 known as The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY). Specifically, the six republics that made up the federation - Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia (including the regions of Kosovo and Vojvodina) and Slovenia.
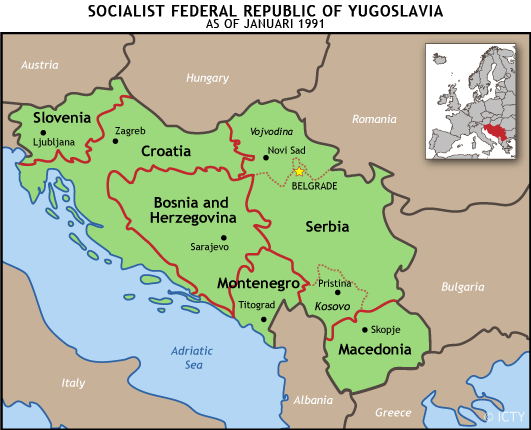
On 25 June 1991, the declarations of independence of Slovenia and Croatia effectively ended SFRY’s existence. By April 1992, the further declarations of independence by two other republics, Macedonia, as well as Bosnia and Herzegovina, left only Serbia and Montenegro within the Federation.
These two remaining republics declared the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (FRY) on 27 April 1992. In 2003, the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia was reconstituted and re-named as a State Union of Serbia and Montenegro. This union effectively ended following Montenegro's formal declaration of independence on 3 June 2006 and Serbia's on 5 June 2006.


